Networks and Connections
Network consists of at least two computers connected to each other and which resources are available for use via other connected computers. There are several different networks, most typical being LAN (Local Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network)
LAN and WAN
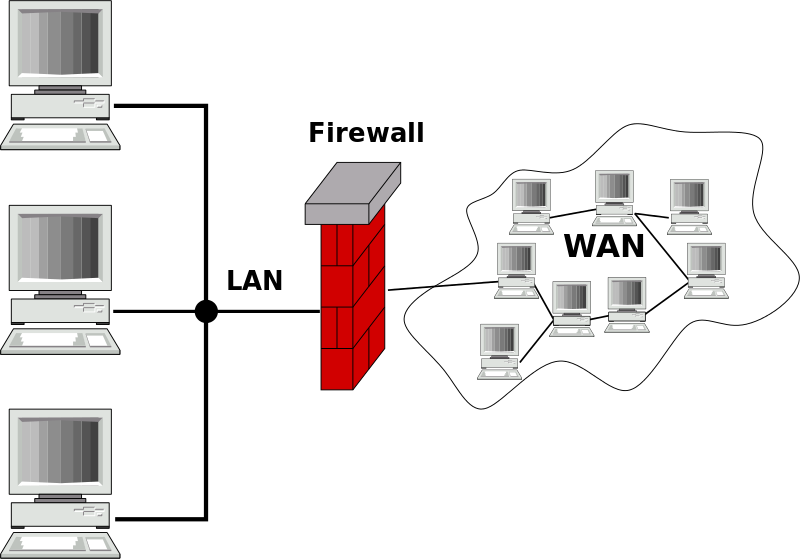
In a local area network workstations are typically connected to one Ethernet network using a switch (connects computers to LAN), router (connects LANs) or hub (connects segments of LAN). Ethernet is a network technique developed by Xerox, DEC and Intel that allows data transfer between computers connected to the network without need to use any external medium. Theoretical maximum speeds are 10, 100 or 1000 Mbps. LANs connected to each other can form a wide area network, WAN.
Also other devices can be used via LAN, e.g. printers and printer services can be shared and used across the network. This applies both organizations but also home users, you are able to create a home network that allows you to use same services from several computers in your network.
Internet, Intranet and Extranet
Internet consists of several networks connected with each other, servers and services provided by them. Quite often internet and World Wide Web (WWW) are considered as being the same thing. Instead, WWW is one of the services of internet. Some services among others are email and file transfer protocol FTP.
Internet thus is a concept of several global, electronic services that are basically free. On the other hand, connection to network is often established using a connection from a service provider, which normally isn’t free of charge. Nowadays organizations, schools and other public service providers (libraries etc.) together with companies are providing free use of network for their customers and members.
Initially, the precursor of internet was created based on needs of US military, thus producing the first network ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) in late 1960s. After this, internet was first used among universities and public institutions. To the public internet came more accessible in 1993 when the first visual web browser was released.
Intranet means an internet-like network of services that is only accessible by users of the organizations LAN or WAN. Access rights to network are granted to employees, students etc. Intranet services are not available when you are connected to a public network, e.g. trying to reach the services from home. Typically the services are provided by one or more servers located in the LAN. Restricting the access is done by using firewalls. A firewall can be one of the servers or another device between LAN and internet, such as a router.
Extranet is a limited section of intranet services (e.g. part of website or a file server) that can be accessed using public network. The user must have credentials to intranet and this information is used to authenticate the right of the user to use the services. In JAMK using Elmo outside JAMK network is provided as an extranet service and it can not be accessed without existing user account.
Internet connections
In order to access internet, a connection must be purchased from an ISP (Internet Service Provider). Mainly two types of connections are available: broadband connections (ADSL, 3G, 4G, 5G) and a fixed-line connection to backbone network (in Finland FUNET, Finnish University Network, which mainly provides network connection to universities and research institutions).
Broadband
Fixed-line broadband connections also come mainly in two types: xDSL (Digital Subscriber Line), of which the consumer version is ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) and a cable modem connection. ADSL uses existing telephone network and cable connection is established using cable TV network. ADSL broadband uses modem (modulator/demodulator) to establish the connections. Modem encodes the digital signal from computer to analogue in order to transfer if using the telephone line. Accordingly, the incoming analogue signal is then converted back to digital. ADSL signal frequency differs from the frequency of phone signals, which is why they can work simultaneously. To have a working ADSL connection, telephone is not needed though, only the network. Data transfer rate in networks are usually expressed as kilobits or megabits /sec (kbps, Mbps). ADSL technique typically provides 1 to 24 Mbps transfer rate for incoming data for private customers, although faster connections are available. In order to use a cable connection, a cable network must be available and have bidirectional functionality. Cable connections normally have higher rates for incoming than outgoing data.
3G, 4G and 5G are mobile broadband connections used often in mobile phones. Data transfer rates are mainly 1 – 8 Mbps in 3G and 10 – 100 Mbps in 4G networks. 4G networks cover well main roads and centers of population, areas of dispersed settlement might have missing connectivity.In these cases the connection is tried to accomplish using another mobile connection like, 3G, Edge or GPRS. In all these cases data transfer rates will be dropping. Transfer rate also is affected by the number of devices connected to a base station. When number of devices increases, the transfer rate is decreased as the connection is shared with other users.
Starting from 2018 some teleoperators have been initiating build of 5G networks in major centers of population in Finland.
HPNA or HomePNA is a technique developed by Home Phoneline Networking Alliance that enables sharing a DSL connection in a housing cooperative using telephone lines. Typically technique is utilized in apartment buildings. Using this technique, the user only needs a HomePNA-adapter instead of an ADSL modem. Building is first connected using a DSL connection which is then shared between the apartments. Drawback in this technique is the fact that number of concurrent users affectst the transfer rate.
The announced data transfer rates are always theoretical maximum rates and the real rates may be 5 – 40 % lower depending on the type of connection. Actual transfer rate is affected by the techniques used (fixed, wireless…) and the network load. Table below contains estimates of actual transfer rates in comparison to theoretical maximum. In order to be able to assimilate the rate with amount of data transferred, the rates are expressed using kilobytes / sec (kBps) or megabytes / sec (MBps) . E.g. 1 Mbit /s = 128 kB/s (1 Mbit = 1024 kbit and 1 B = 8 bit).
| Data transfer
rate |
Theoretical
maximum |
Estimate ofactual rate |
|---|---|---|
| 256 kbps | 32 kBps | 25 kBps |
| 512 kbps | 64 kBps | 50 kBps |
| 1 Mbps | 128 kBps | 100 kBps |
| 2 Mbps | 256 kBps | 200 kBps |
| 8 Mbps | 1024 kBps | 800 kBps |
| 10 Mbps | 1,25 MBps | 1 MBps |
| 24 Mbps | 3 MBps | 2.4 MBps |
| 100 Mbps | 12,5 MBps | 10 MBps |
Think over! What kind of networks are you using?
Material progressed
Material progressed